PyGTK CD Ripper Tutorial - Part 5
Part 1 of this pygtk tutorial stopped with a working toolbar and two place
holders. Part 2 of this tutorial extended this minimal UI with a list of
songs which was created using GTK ListView. Part 3 showed how to gain better control
on ListView. Part 4 added some final polish to the UI and added an empty Preferences
Dialog. This part of the tutorial will create the following preferences dialog:
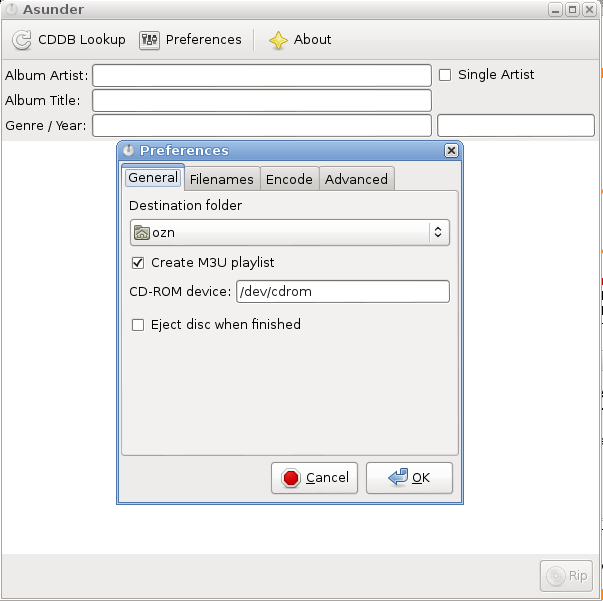
To begin with, the preferences Dialog has to contain a gtk.Notebook, which is created with:
notebook = gtk.Notebook()
In order to keep a well organized and readable code, the creation of the notebook instance is
defined in a class method of PrefDialog and called in the init method of the class:
def insert_notebook(self):
"""
demonstrate a gtk notebook
"""
notebook = gtk.Notebook()
...
def __init__(self, window):
"""
initialize the preferences dialog
"""
# title, parent, flags (0, for defaults), no buttons
self.dialog = gtk.Dialog("Preferences", window, 0,
(gtk.STOCK_CANCEL, gtk.RESPONSE_CANCEL, gtk.STOCK_OK, gtk.RESPONSE_OK))
self.dialog.set_default_size(250, 300)
# creat the notebook instance
self.insert_notebook()
response = self.dialog.show_all()
response = self.dialog.run()
if response == gtk.RESPONSE_OK:
print "The OK button was clicked"
elif response == gtk.RESPONSE_CANCEL:
print "The Cancel button was clicked"
self.dialog.destroy()
Right now, this code does not do much. It attaches the notebook instance to the vbox which was automatically
created inside the Dialog window. A notebook can have multiple pages, and each page in turn can have widgets
attached to it with the packing method demonstrated before:
def insert_notebook(self):
"""
demonstrate a gtk notebook
"""
notebook = gtk.Notebook()
lables = []
for page in ["General", "File Names", "Encode", "Advanced"]:
# later, we can replace widget with a vbox, and then
# the road is wide open to start packing other widgets inside it!
widget = gtk.Label(page + " Inside")
widget1 = gtk.Label("Second Label")
vbox = gtk.VBox(False)
vbox.pack_start(widget)
vbox.pack_start(widget1)
label = gtk.Label(page)
notebook.append_page(vbox,label)
self.dialog.vbox.pack_start(notebook)
The above method will create the following Preferences Dialog:
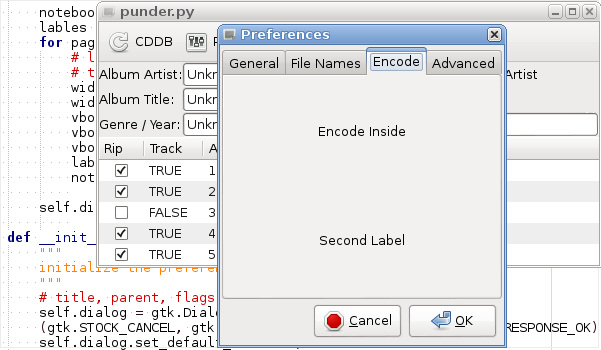
Download the complete code for the preferences dialog.
However, this notebook is still quite primitive. The widgets added are just text widgets and the notebook tabs titles are not given. To access a notebook's tab the following method can be used:
# index is an integer, with N-1 representing the last page
# e.g. for a notebook with 4 page, idx can be 0,1,2 or 3
tab = notebook.get_nth_page(idx)
The setting the tab's label is done with:
notebook.set_tab_label_text(tab, "some title you would like to choose")
Once a notebook page is direct accessible, it could also be manipulated, and widgets
can be directly attached to it. Below, a gtk.FileChooserButton is added to the first
tab (General). The file choose button, is not directly added to the page. Rather, it is
packed inside a VBox instance. Into the same VBox gtk.Alignment instance, is also
attached. This gtk.Aligment contains a flushed left gtk.Label.
general = notebook.get_nth_page(0)
filechooserbox = gtk.VBox(False)
alignment = gtk.Alignment(0,0)
filechooserlabel = gtk.Label("Destination folder")
alignment.add(filechooserlabel)
filechooserbutton = gtk.FileChooserButton("Destination folder")
filechooserbutton.set_action(gtk.FILE_CHOOSER_ACTION_SELECT_FOLDER)
filechooserbox.pack_start(alignment)
filechooserbox.pack_start(filechooserbutton)
general.add(filechooserbox)
This addition to the method insert_notebook will create the following preferences Dialog:
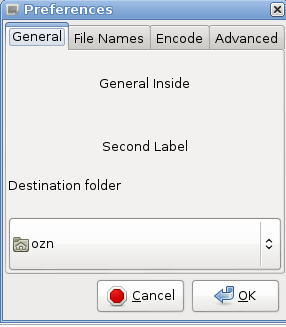
Notice, that the new VBox and the gtk.FileChooserButton where added to the existing labels!
Download the complete code for the preferences dialog with a FileChooserButton.
The complete assembly of widgets, is then added with the following add_notebook method:
def insert_notebook(self):
"""
populate the notebook with widgets.
"""
notebook = gtk.Notebook()
for idx, page in enumerate(["General", "File Names", "Encode",
"Advanced"]):
# later, we can replace widget with a vbox, and then
# the road is wide open to start packing other widgets inside it!
widget = gtk.Label(page + " Inside")
widget1 = gtk.Label("Second Label")
vbox = gtk.VBox(False)
vbox.pack_start(widget)
vbox.pack_start(widget1)
label = gtk.Label(page)
notebook.append_page(vbox)
pg = notebook.get_nth_page(idx)
notebook.set_tab_label_text(pg, page)
# here is how one can access a single tab
another_label = gtk.Label("Accessed")
pg.add(another_label)
# populate general tab with proper stuff
generalpage = notebook.get_nth_page(0)
generalvbox = gtk.VBox(False)
alignment = gtk.Alignment(0,0)
filechooserlabel = gtk.Label("Destination folder")
#filechooserlabel.set_justify(gtk.JUSTIFY_LEFT)
alignment.add(filechooserlabel)
filechooserbutton = gtk.FileChooserButton("Destination folder")
filechooserbutton.set_action(gtk.FILE_CHOOSER_ACTION_SELECT_FOLDER)
generalvbox.pack_start(alignment, False, False, 0)
generalvbox.pack_start(filechooserbutton, False, False, 0)
generalpage.add(generalvbox)
# add check button for making m3u playlist
make_playlist = gtk.CheckButton("Create M3U playlist")
# make default as true
make_playlist.set_active(True)
generalvbox.pack_start(make_playlist, False, False, 0)
# add the cdrom drive entry inside an hbox
hbox = gtk.HBox(False)
cdrom_label = gtk.Label("CD-ROM device: ")
cdrom = gtk.Entry(128)
cdrom.set_tooltip_text("Default: /dev/cdrom\n"
"Other example: /dev/hdc\n"
"Other example: /dev/sr0")
hbox.pack_start(cdrom_label, False, False, 0)
hbox.pack_start(cdrom, False, False, 0)
generalvbox.pack_start(hbox, False,False, 0)
eject_cd = gtk.CheckButton("Eject disc when finished")
generalvbox.pack_start(eject_cd, False,False, 0)
self.dialog.vbox.pack_start(notebook)
This code will produces the following General notebook tab:

Again, the new widgets are all added to the previous labels, and the method becomes quite long and messy.
This calls for some code clean up and reorganising. First, since all the pages (tabs) in the notebooks are
going to have at least one widget, it makes since to create them and attach a gtk.VBox to each. Further,
since long methods are hard to follow, it makes since to separate all the code that adds widgets to the
General page. This code should be migrated to it's own method, e.g. def General_Page(self). Customizing
other pages would be similarly done in extra methods, e.g. def FileNames(self) and so on.And Finally, since,
the notebook instance should be accessible to all the methods that customize the pages, it should become
an instance variable, e.g., instead of:
notebook = gtk.Notebook()
the notebook is created as:
self.notebook = gtk.Notebook()
And the complete method to create the notebook is now:
def insert_notebook(self):
"""
create a notebook with 4 pages, each containing a gtk.VBox.
"""
self.notebook = gtk.Notebook()
for idx, page in enumerate(["General", "File Names", "Encode",
"Advanced"]):
# later, we can replace widget with a vbox, and then
# the road is wide open to start packing other widgets inside it!
vbox = gtk.VBox(False)
self.notebook.append_page(vbox)
pg = self.notebook.get_nth_page(idx)
self.notebook.set_tab_label_text(pg, page)
self.set_general_page()
self.dialog.vbox.pack_start(self.notebook)
the method set_general_page():
def set_general_page(self):
"""
add widgets to the page General
"""
# populate general tab with proper stuff
generalpage = self.notebook.get_nth_page(0)
generalvbox = gtk.VBox(False)
alignment = gtk.Alignment(0,0)
filechooserlabel = gtk.Label("Destination folder")
#filechooserlabel.set_justify(gtk.JUSTIFY_LEFT)
alignment.add(filechooserlabel)
filechooserbutton = gtk.FileChooserButton("Destination folder")
filechooserbutton.set_action(gtk.FILE_CHOOSER_ACTION_SELECT_FOLDER)
generalvbox.pack_start(alignment, False, False, 0)
generalvbox.pack_start(filechooserbutton, False, False, 0)
generalpage.add(generalvbox)
# add check button for making m3u playlist
make_playlist = gtk.CheckButton("Create M3U playlist")
# make default as true
make_playlist.set_active(True)
generalvbox.pack_start(make_playlist, False, False, 0)
# add the cdrom drive entry inside an hbox
hbox = gtk.HBox(False)
cdrom_label = gtk.Label("CD-ROM device: ")
cdrom = gtk.Entry(128)
cdrom.set_tooltip_text("Default: /dev/cdrom\n"
"Other example: /dev/hdc\n"
"Other example: /dev/sr0")
hbox.pack_start(cdrom_label, False, False, 0)
hbox.pack_start(cdrom, False, False, 0)
generalvbox.pack_start(hbox, False,False, 0)
eject_cd = gtk.CheckButton("Eject disc when finished")
generalvbox.pack_start(eject_cd, False,False, 0)
The total length of the code is only a bit shorter. However, the code regarding the page General is completely
encapsulated inside it's own method, and is called via:
self.set_general_page()
The notebook itself is created with four pages, each containing a gtk.VBox widget. This makes modifying
other pages quite straight forward, but avoids a long and complicated method to create a fully functioning
notebook rich with widgets. The complete code for this part, demonstrating a gtk.Notebook with
pages and embedded widget can be found in the git tag NotebookwithGeneral_Tab.
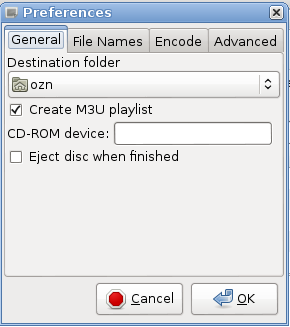
The next tree pages of the notebook are still empty. However, in the original application asunder
they all contain gtk widget which I found a bit tricky to control (namely, gtk.Frame). Hence, these pages will be
populated with these multiple gtk.Frame widgets in the next part of this tutorial, and for now, the Preferences Dialog
contains one page with the title General and looks like that:

Share this post: